What is urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is the loss of bladder control. This can vary from slight loss of urine to the complete inability to control urine. Most commonly, urine is lost due to sneezing, coughing, or laughing. The four different types of urinary incontinence are:
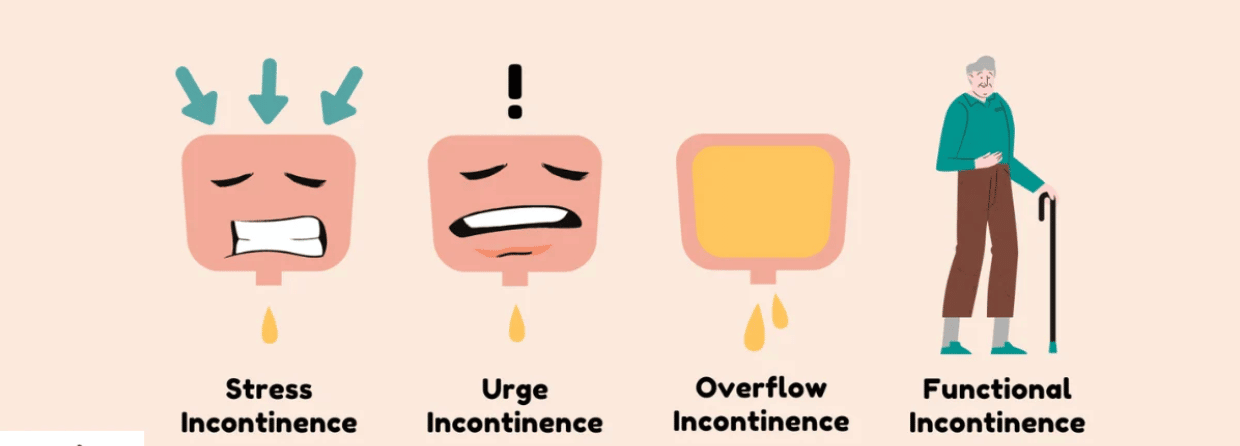
- Stress Incontinence: the leaking of urine exercise, coughing, sneezing, or laughing
- Urgency Incontinence: the inability to hold urine long enough to reach the restroom
- Overflow Incontinence: the leaking of urine because the quantity produced exceeds the bladder’s capacity to hold it
- Functional Incontinence: urinary leaking due to not reaching the restroom in time because of physical conditions (most common in older adults)
What causes urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence is not just caused by aging, but is most common in older individuals. Often times, it is caused by changes in body function, that may result from diseases, medication, or the onset of illness. Another factor to be aware of, is that sometimes it is the first and only symptom of a urinary tract infection. In women, stress incontinence can occur from pregnancy, childbirth, or after the hormonal changes of menopause.
What are some symptoms?
Each individual may experience urinary incontinence symptoms differently. Some symptoms include:
- needing to rush to the restroom/losing urine if not made in time
- feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- leaking of urine that prevents activities
- urine leaking when coughing, sneezing, or laughing
- urine leakage with movements or exercise
- constant sensation of wetness without sensation of urine leakage
- need to urinate often
- problems passing urine
How is urinary incontinence diagnosed & treated?
For individuals with urinary incontinence, it is important to consult a trusted health care provider. Often times, you will be referred to a urologist or a urogynecologist, which are doctors who specialize in disease of the urinary tract. You may be asked to keep a bladder diary or complete a post-void residual measurement test. Urinary incontinence is diagnosed with a complete physical examination that focuses on the urinary and nervous systems, reproductive organs, and urine samples.
Treatment may include behavioral therapies, like bladder training and toileting assistance. Bladder training teaches individuals to resist the urge to void, gradually expanding intervals in which to void. Toileting assistance is creating and sticking to a toileting schedule. You can also make diet modifications, removing bladder irritants such as coffee, alcohol, and citrus fruits from your diet. Another common treatment is physical therapy and pelvic muscle rehabilitation. This is where you strengthen your pelvic floor and improves pelvic muscle tone to reduce urine leakage. Treatment may also include medication, surgery, or a pessary, which is a small rubber device that is worn inside the vagina to reduce leakage.




